Home » Disdvantages of VPN
Disadvantages of VPN
UPDATED February 2026
Advertising Disclosure
![]()
Many or all of the companies featured provide compensation to us. These commissions are how we maintain our free service for consumers. Compensation, along with hours of in-depth research, determines where & how companies appear on our site.
Advertising Disclosure: Many or all of the companies featured provide compensation to us. These commissions are how we maintain our free service for consumers. Compensation, along with hours of in-depth research, determines where & how companies appear on our site.
These days, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) are more popular than ever. The number of people using VPNs is increasing every day. Despite that many people still, don’t know how VPN services work and which pitfalls they should be aware of. In this article, we’re going to discuss the disadvantages of VPNs in depth.

What Is a Virtual Private Network?
A VPN is an online service we use to unblock censored parts of the Internet and also geo-restricted content. Many people also VPNs to protect their online data from hackers and government surveillance. A VPN is able to do that by encrypting online traffic and hiding the real IP address of its users.
EXPERT QUOTE
"When using unencrypted connections, internet bad guys can sniff on your traffic to spy, steal data, hijack devices, and even steal identities. A VPN can however encrypt your traffic using standards like the AES 256-bit protocol to make your data transfer secure."

Joel Timothy
Cyber-Security and VPN Expert
Advertising Disclosure
The information we provide you is free of charge and a result of extensive research by our product experts. We use affiliate links in our site that provide us with referral commissions. While this fact may not influence the information we provide, it may affect the positioning of this information.
VPN Alternatives
How Do VPNs Work?
A VPN service relies on a VPN server and a VPN client to start a secure connection for you. Users have to install the client on their device to start using the service. These users then connect to the VPN server of their choice to access the content of their desired country. When the connection gets established, an encrypted tunnel gets created between the client and the server. Every connection request users send through the client to the web get encrypted before being sent to the server. Afterward, the server decodes these requests and forwards them to the web. The server then receives the desired information back and sends that information after encrypting it again. Finally, the VPN client on the user’s device decrypts received information so that the user is able to use that information.
Disadvantages of VPNs
A VPN has plenty of useful features such as geo-blocking abilities, providing a private and secure channel. to exchange information and much more. Despite that, there are many things VPNs still have to work on to get better. Though some VPNs overcome these shortcomings and live up to their promise, many VPNs still have shortcomings which end up harming users. Here are some of the apparent disadvantages of VPN services have:
VPNs Slow Down Speed
There are many factors that affect how your connection speed will get affected after using a VPN. Things like the distance from the VPN server, the strength of encryption is, and the type of VPN protocol you have will take a hit on your speed.

Your Internet connection speeds will almost certainly slow down whenever you use a VPN service. It’s not necessary that your VPN speed will cripple down every time. Most times, these slowdowns are not that noticeable. However, you still have to be prepared for a potential decline in speed if you use a VPN.
Some VPNs Can Put Your Privacy At Risk
The core reason for using VPNs is ensuring user privacy and a secure connection. These services are meant to protect online data and user identity. However, if people don’t do their research properly, they end up picking a service that does the total opposite of that. Generally, the culprits are inexperienced providers and most times, free VPN services. You can identify such services by keeping an eye on usual signs like buggy applications, no tutorials, or support. Moreover, these VPNs don’t provide clear details about the type of security they offer. Similarly, free VPNs are especially dangerous as they’re offering a service for free. As we all know, no business offers services for free unless they’re benefiting from it in some way. Free services are most likely to get you in trouble. This happens because these free VPNs have lackluster encryption mechanisms that can expose users to malware. Moreover, a number of free VPN services keep a log your online activities. It doesn’t seem much at first, but it endangers the privacy of users. Ultimately, it defeats the purpose of using VPNs. You can avoid this issue easily by choosing a paid VPN service that has no logs. Paid VPN services also offer high-end security protocols such as OpenVPN and SoftEther. Moreover, these VPN services also have advanced encryption features, protections from various leaks, and handy kill switches.
High-End VPNs Are Expensive
We understand that free VPNs are clearly something you should stay away from. Therefore, VPN users have to rely on high-end VPN services to get by. However, these premium VPN services are paid, and they’re usually not as inexpensive as you’d assume. Quality VPN service demands high maintenance and operation cost. VPN providers have to ensure that hundred of their servers worldwide keep running without interruption. These services also have to face pressure from the state governments and surveillance agencies. So, it’s understandable that these services cost a bit more. Still, if you’re short on cash, this can be a problem, especially when some providers charge up to $9-12 per month. These costs can also add up in the long run and increase as you continue to use the service. However, you can benefit from premium VPN services by selecting long-term subscriptions. It can help you get the best value for money, along with the most premium services available in the VPN market. VPN such as UltraVPN allow you to use their service for just $2.99 a month on an annual subscription. Nord VPN offers the same price, but you’ll have to commit for three years. Unless you’re willing to stick to a certain VPN service, premium VPNs services will generally be expensive. VPNs Don’t Get Supported on All Platforms Most VPN services work on most popular platforms such as Windows, iOS, macOS, or Android. However, these VPN services rarely give attention to other operating systems and devices that are not as popular. Most VPN services fail to offer support to platforms Linux, Chromebook or Boxee Box. Moreover, devices such as Amazon Fire TV and some routers don’t get support from some VPNs. VPN providers tend to ignore these platforms because only a small section of their customer-base uses these platforms. As a result, people who are accustomed to these platforms suffer. They have great difficulty in using VPN services for their devices. To use VPN services on outlying platforms or devices, VPN users have to do a lot of configuration manually. Most connections have to be set up through manual controls which are extremely inconvenient. These users eventually give up after failing to set manual connections.

As discussed before, some platforms don’t have any native support for VPN applications. Devices such as gaming consoles, set-top boxes, and some smart devices have to connect to a router for access to VPN services. Even when you’re setting up a VPN connection to a router, you’ll face many problems. Setting your VPN on the router is really complex not everyone can do it. Moreover, these manual configurations need compatible firmware to work on a specific router brand.
Surveillance Agencies Can Break VPN Encryption
Many people aren’t aware that surveillance agencies hire some of the world’s most capable hackers to get into systems. Agencies like the National Surveillance Agency have the technology to break a VPN’s encryption mechanism. The majority of VPNs that use 1024-bit encryption use the Diffie-Hellman mechanism for cryptographic key exchange. This key exchange is an integral component of encryption and is necessary to encode and decode information on both sides of the exchange. However, it seems that this encryption mechanism is not free from faults. The method uses a restricted number of prime numbers to make the cryptographic exchange possible. Though it still is not easy to crack this algorithm, highly-skilled hackers can still get through it. Experienced hackers can exploit this flaw to break this encryption through various algorithm breaking techniques. In the end, these hackers are able to snoop on the information by decrypting these texts. Researchers such as Nadia Heninger and Alex Halderman further explain: “Breaking a single, common 1024-bit prime would allow NSA to passively decrypt connections to two-thirds of VPNs and a quarter of all SSH servers globally. Breaking a second 1024-bit prime would allow passive eavesdropping on connections to nearly 20% of the top million HTTPS websites. In other words, a one-time investment in massive computation would make it possible to eavesdrop on trillions of encrypted connections.” Edward Snowden – the famous American whistleblower and champion of international privacy activists, expressed his concerns regarding the NSA. Snowden had warned the world about the NSA’s ability to snoop on encrypted connections even before this research was published. All in all, VPNs aren’t as secure as most VPN users think. However, having an AES 256 bit algorithm certainly helps in retaining your privacy. Moreover, you need the world’s top hacking minds to break through these encryption algorithms. So, a general user doesn’t have to worry about their personal information.
ISPs Can Block VPN Connections with Impunity
It’s not uncommon for users to try accessing blocked media in a server by using a VPN. VPNs are great at bypassing local and global restrictions on content because of their ability to tunnel connections from one country to another. VPN’s bypass these restrictions through their designated servers placed in other countries. However, your ISPs can expand their restriction if they’re able to pick where these servers are. The ISPs can block VPN connections as a whole to stop people from bypassing restrictions set up by the ISP.
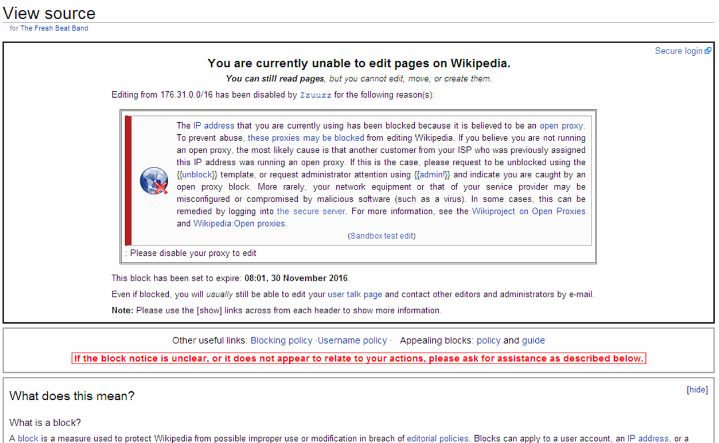
An ISP blocking VPN connections are not obvious, but you can check whether your ISP is doing it by going on streaming websites. Streaming a TV show or movie via your VPN can help you find out whether or not your ISP is blocking the VPN. If it doesn’t work when a normal unencrypted connection is working, then it means that your ISP has blocked your VPN. Moreover, ISPs in the US have the ability to snoop on user activities and sell the data to third parties. High-end VPN services don’t allow this and ensure that ISPs can’t see your activity. However, if you’re using a low-quality VPN service, then your personal data is probably in the hands of a third-party.
Free VPNs – the Bane of Privacy
As we’ve discussed before, you should be wary of VPN services that are complete. On one hand, there are paid VPN services who announce a free VPN service to enable users to experience their VPN service. Premium VPN services such as UltraVPN also have free versions that provide top-of-the-line features to its users. Still, these services are somewhat limited, and you’ll have to buy the paid plan to avail the complete package. Moreover, we don’t recommend long term use of these free versions of paid applications. A paid subscription service is more advanced and will deliver far better results. On the flip side, there are other malevolent VPN services that sell user data in the pretext of free service. While it might be fun to get free services for yourself, but a total disregard of your privacy will be extremely harmful.

One of the most foretelling signs that a free VPN service is up-to-no-good is that it won’t be transparent. They will not tell you how they make money from the services they’re providing. In most cases, when they are not selling you a product, then most likely you are their product yourself. These free VPNs will simply sell your data to their affiliated/partnered companies even to third parties; whoever is willing to pay the most. There also have been instances where free VPNs have gotten caught in malicious practices. These VPNs have been found injecting ads and referring affiliate traffic by CSIRO researchers. You normally associate the word privacy with VPNs in general. However, the presence of such free VPN services establishes the complete opposite of that perception. These services are not only harmful to people using them but also for the image of the VPN industry as a whole.
Geo-Blocking Restrictions Target Known VPN Servers
In the early days, VPN services had little problem bypassing geographic restrictions. Now, however, the situation is changing. It is becoming increasingly difficult for VPN services to bypass these restrictions. You can easily observe this if you take a look at content streaming websites all around the world. For instance, in the past, Netflix still had geographic restrictions on content. However, it was easy to bypass this obstruction by simply logging into a VPN server that is inside the restricted country. This way, Netflix servers were fooled into believing that you were accessing the restricted content from the country where it’s allowed.

These days, Netflix authorities have become stricter in this process. They have set up blocking mechanisms that thwart poorly directed bypassing mechanisms. In other words, Netflix is cracking down on VPN services. Only a handful of VPN services are able to bypass these restrictions now. Many of these VPN services put their ability to bypass streaming services as their advertising gig. It’s not just Netflix; other services have developed similar hard-to-crack mechanisms. The BBC iPlayer prevents users from outside the UK from accessing restricted content. If you try to view content on the UK-version of BBC iPlayer from an overseas area, you’ll get blocked through a polite message. However, using a U.K.-based VPN server will result in a similar response. All these streaming services have developed a blacklist of VPN servers. They establish these lists by checking VPN providers and logging their server IP addresses. After these IP addresses get blocked, it’s impossible for users to access them again unless the VPN service invests in other servers.
Handful No-Log VPNs
VPNs tend to seek attention by promising whatever they can. Most VPNs promise whatever they can get away with, which is unfortunate. One of the most eye-catching features in a VPN’s arsenal is its no-log policy. A no-log policy is essential in maintaining the privacy of users. After all, why would anyone want to pay for anonymity if the logs kept by the VPN service can expose you? In reality, only a handful of VPNs truly have a no-log policy. Though it’s next to impossible for VPNs to be 100 percent free of logs, these high-end services still manage to subvert any information that might lead back to you. Their no-log policy allows them to delete any information that can be used to identify you personally. However, these premium services are an endangered minority. In other cases, most VPNs are helpless to information leaks despite having a no-log policy. You see, many VPN services use third-party servers to make their service available in as much as countries as possible.

It means that while your VPN service may not keep logs of your activity, it’s entirely possible that third-parties owning these servers are. Though most server owners keep logs to improve the server performance, it is distressing for a privacy-sensitive user. Keeping logs of all the incoming and outgoing traffic is essential for server management. Without keeping temporary logs, it’s impossible for a server to manage DNS requests, troubleshoot connections, or prevent abuse. Knowing that there is a log of your activity somewhere in the world might sound innocuous, but it can be deadly if you’re a political dissident. However, most of these logs are temporary and get removed from the server sometime after your session ends. Regardless, it’s worth looking at VPN’s privacy policy to know what kind of logs they save. You can also find out which information they are admitting to collect.
Data Mining Personal Information
We live in a post-privacy world of pervasive social-media sharing. There are several ways marketing agencies target us. These companies extract our personal information through browser-cookie targeting and quantify consumer-intention profiling for each user. This new marketing strategy has its roots in the intrusive collection of data for marketing purposes. They do not hesitate from extracting our personal data and logging them into their databases. Moreover, these companies use normal websites to gather information about us and use data mining techniques to micro-target consumers.

Though reputable sites don’t do this, you can never know. VPNs have been designed to counter these data extraction strategies and protect the identity & information of these users. However, some VPN services go as far as providing this data themselves. Most of the VPN services engaged in this malpractice are either free VPNs or low-cost VPNs trying to maximize their revenue. These services increase their profits by directly selling your information to advertising companies that spam you with targeted marketing in response. Getting your information sold by these companies is extremely worrying. However, you can also get tracked with the help of this information as well. Whatever the case is, your information is being exploited without your consent. We’ve already discussed how this is a problem with free VPNs, but people don’t expect the same behavior from a paid solution. However, paid solutions engaging in this malpractice is not uncommon, and plenty of these services engage in this act. Selling user information is not only a breach of trust but also against the basic tenets of a VPN service. By sharing information about its users, these VPNs make extra money, and you get spammed in return. You will be able to observe specialized advertisements targeted to you on the sites you visit.
All VPNs Are Not Completely Anonymous
As we’ve discussed before, VPN encryptions are not as impregnable as most VPN users used to assume. We talked about how the NSA can break through encryption algorithms by using ingenious hacking techniques to spoof on connections. However, issues with anonymity in VPNs are not restricted to encryption only. One of the biggest privacy issues with a VPN is IP leaks during connections. An IP leak is the leakage of the user’s real IP address when he or she is connected to a VPN service. It occurs when a user’s computer unknowingly accesses default servers instead of anonymous VPN servers. For instance, when you’re trying to access some geo-restricted content, you log into the VPN. You will select the country from where you want to access the service. The VPN service will relay your connection to the country you selected. Usually, this is enough to convince a service to allow you access for restricted content. However, if you still fail to access that content because of geo-restrictions, then the service is actually tracking your original IP. This is a clear sign that your VPN isn’t hiding your IP effectively and leaking your original IP. This is a real problem with some VPNs. Most IP leak types affect one network protocol at one time or another protocol on a mobile device. Still, high-quality VPN providers have internal mechanisms that minimize the likelihood of IP leakages. Likewise, your connection can suffer from a DNS leak which can expose your original IP to the DNS server. It usually happens when user requests are being sent to an unsafe DNS server. This DNS server is normally under control of your VPN provider. Some VPNs like Nord VPN have built-in DNS leak protection. They provide custom DNS servers instead of leaving you at the mercy of your ISP’s DNS server. Moreover, these servers have special technologies that ensure DNS requests are always routed through a secure and encrypted VPN tunnel. However, most VPNs fail at curbing leaks in their service. So users should be careful before choosing their VPN services for the first time. Still, there are other issues that compromise the anonymity of users. We’ve already touched the trust issue in VPNs. Many VPNs say one thing in their advertisements and another in their privacy policy. There is a real question mark regarding whether VPNs do their best in keeping your data private or not. However, there’s a more serious problem, one that everyone else overlooks. A VPN connection is only secure and private between the user’s computer and the VPN provider’s server. Beyond that, anyone can identify you. And it’s not limited to the account you log in with. Even data transmitted between the destination website and the VPN server can be read if it’s not properly encrypted. We’ve already discussed what security agencies can do with encryption. Something that is most concerning is the fact that a VPN provider can see your destination. It’s not obvious who is going on which website, but the websites you access and services you use get recorded on the website regardless.
What Can You Do To Have Private and Safe Connections?
We’ve covered all the hazards a VPN service can have, and things seem bad for most VPN services. However, as restrictions and exploitations are increasing, VPNs are also improving themselves to become more secure and private. They are already using several techniques such as protocol obfuscation. This step is theoretically more secure than the TLS/HTTPS/SSL that is used on a wide scale all around the world. Moreover, you can also build a VPN in a computer’s operating system and establish authentication for connections. Moving on to HTTPS protocols should also help when you’re logging in a website. Another useful trick to improve an underperforming VPN is coupling it with a Tor browser. VPN and Tor browsers can come together to provide users with the ultimate privacy experience. It is currently the most secure and private way to connect to the internet. Although it’s slow, VPN services can improve their speeds and overcome these limits in the foreseeable future. This is why TOR is becoming increasingly popular among users that have privacy concerns, so it makes sense to merge both privacy methods into a single powerful solution.
What about VPNs – Should We Keep on Using Them?
Considering all the disadvantages of VPNs we’ve discussed, it’s pretty obvious that not all VPN is perfect. However, some premium VPNs overcome all problems and allow their users to enjoy secure online connections and free access to censored and blocked content. When you’re choosing a VPN connection, you should look for the VPN that suits your needs the best. Most times, it will be the VPN that provides the most premium features such as torrenting, access to streaming sites, and specialized IPs. However, you should not overlook necessary security features such as DNS protection. You should only choose a VPN service if it truly has a no-log policy. It should also have features like kill switches – that protect user data when the secure connection gets abruptly terminated. All in all, a VPN service with high-speed connections, fast VPN protocols like OpenVPN and unrestricted bandwidth is a great option. One such VPN is Nord VPN. The VPN provides an extensive number of servers all around the world which number up to 5200 – unmatched by any other VPN. More so, independent authorities have verified that Nord VPN has a true no-log policy and does a complete job at maintaining user privacy. If you want to benefit from premium features with a discounted price, visit their website and get Nord VPN now.
Protect Your Internet Browsing
GET NORD VPN NOW!

98%
OVERALL RATING

Advertising Disclosure
The information we provide you is free of charge and a result of extensive research by our product experts. We use affiliate links in our site that provide us with referral commissions. While this fact may not influence the information we provide, it may affect the positioning of this information.