Home » The 21 Most Alarming Cyber Security Statistics
21 Alarming Cybersecurity Statistics In 2026
UPDATED February 2026
Advertising Disclosure
![]()
Many or all of the companies featured provide compensation to us. These commissions are how we maintain our free service for consumers. Compensation, along with hours of in-depth research, determines where & how companies appear on our site.
Advertising Disclosure: Many or all of the companies featured provide compensation to us. These commissions are how we maintain our free service for consumers. Compensation, along with hours of in-depth research, determines where & how companies appear on our site.
Cyber security issues are growing in prominence worldwide. People are worrying about how they can remain safe in a world where we are surrounded by interconnected devices. From smart phones to smart homes; anything can become a tool to invade our privacy and monitor our behavior. This concern is not without cause either.

In the last few years, cyber criminals have tampered into major elections and debilitated longstanding businesses. We cannot ignore the extent to which cyber warfare can influence our lives.
Understanding what kinds of attacks are prevalent in today’s world will help you take necessary actions to protect yourself. In this article, we discuss the 21 most alarming cybersecurity statistics in 2026.
EXPERT QUOTE
"When using unencrypted connections, internet bad guys can sniff on your traffic to spy, steal data, hijack devices, and even steal identities. A VPN can however encrypt your traffic using standards like the AES 256-bit protocol to make your data transfer secure."

Joel Timothy
Cyber-Security and VPN Expert
Advertising Disclosure
The information we provide you is free of charge and a result of extensive research by our product experts. We use affiliate links in our site that provide us with referral commissions. While this fact may not influence the information we provide, it may affect the positioning of this information.
VPN Alternatives
1. Email Hackers use Microsoft Office extensions as the most malicious file extension.
Microsoft Office is one of the most recognized and widely used software products in the world. So, there’s no surprise that hackers use the brand’s file extensions in their malicious emails.
Cisco reported in their 2018 Annual Cyber Security Report that Microsoft extension were the most malicious file extensions in emails. The most popular file extensions among email hackers were Microsoft Word, PowerPoint and Excel formats.
Traditionally, hackers use .exe files to distribute malware across the internet. However, email service providers realized this and now block any .exe file in their emails. This has forced cybercriminals to improve and come up with new ways to spread malware through emails.
As a result, Microsoft’s popular formats have become the premium choice for hackers. This is dangerous because people tend to trust an attachment that has a Microsoft extension. Hackers do this to mask their malicious macro code hidden in these documents from email security and antivirus protocols.
In the report, we can see that the majority of malicious file extensions (38%) are Microsoft Office extensions. The next most dangerous file formats are the .zip and .jar extensions. They account for 14% of the total malicious file formats. In normal cases, archive files use such file formats. However, hackers exploit these formats to insert malicious code.
The website has a structured and clean interface that makes it easy to use. Users can benefit from multiple filters to streamline their searches and make the search results more accurate and efficient. The filters that focus on genre and year-of-release can help you find your all-time favorite films easily. Therefore, Solar Movies stands out as a great platform for online streaming.
2. Americans regard Cybercrime to be a more imminent threat than violent crime.
A recent Gallup survey found that the majority of Americans feel that is an imminent threat. Gallup conducted this extensive survey over the period between 2000 and 2018. The report is comprehensive in the sense that it has diverse data which spans across 18 years.
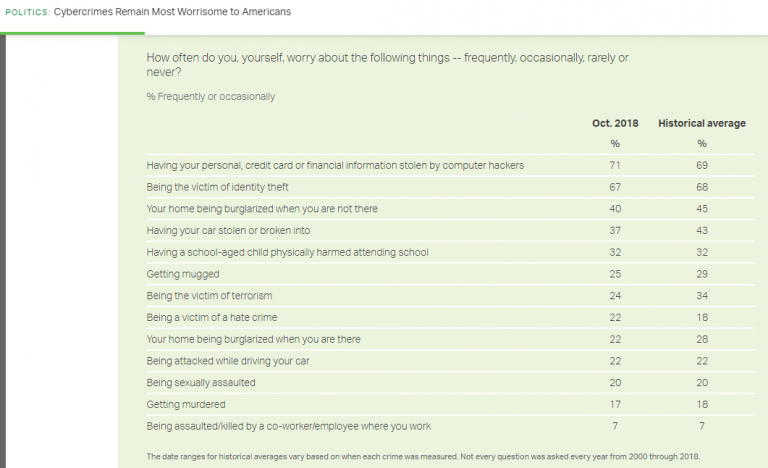
Respondents in the survey suggested that they’re more likely to be a victim of cybercrime than violent crime. This is interesting because this list included threats such as burglary, being sexually assaulted and being a victim of terrorism. According to this report, people worry more about being hacked and having their identity stolen. You can see the following statistics in this report:
- 71% of Americans fear that their personal, credit card or financial information can get compromised. The ratio has risen from where it was before. This suggests people realize that the threat of being hacked online has increased due to massive digitalization.
- 67% of citizens suggest worry that they will become victims to identity theft. Identity theft it is still one of the major concerns in today’s world. In spite of popular belief, identity theft is more than having your identity used by someone else on social media. In the corporate world, if someone manages to impersonate you, they can get access to critical systems. This can incur in a financial loss and destroy a company from within.
- Having their home intruded in their absence is the third most prevalent cause of worry for Americans. Almost 40% people reported burglary as an imminent danger.
- After the gruesome events of 9/11, there was public fear regarding terrorist attacks in the US. However, this has dropped over time. Now 24% of Americans fear being victims of terrorism opposed to the historic figure of 34%.
- 17% people worry being a victim of murder.
- Despite the detection of several harassment cases through the #MeToo movement, sexual assault isn’t a major concern for most people. 20% of people worry that they will become victims of a sexual assault.
- 7% people still fear getting assaulted by their co-workers.
- Violent acts such as getting murdered, getting sexually assaulted or becoming a victim of terrorism were rated as secondary threats. The majority of people don’t believe that these events are an imminent threat to their well being.
3. Almost 73% of the businesses are not prepared to deal with cyber attacks.
As we have discussed before, data breaches cost organizations millions of dollars on average. On top of that, frequency of cyber attacks is increasing each year and doesn’t seem to stop at any point. Yet 7 out of 10 companies are still not prepared to respond to cyber attacks.
The Hiscox Cyber Readiness Report studied more than 4000 organizations in 2018. The survey extended to technologically-advanced countries such the US, the UK, Germany and Netherlands. However, most of these organizations were unprepared for a cyber attack. Unless these organizations establish mechanisms to tackle cyber security issues, they will have to bear losses of millions of dollars.
4. Malicious cyber attacks are the main cause behind data breaches.
Despite popular belief, cyber attacks by hackers are not responsible for 100% of data breaches. There are several factors that can cause systematic data breaches. The following are the most prevalent data breach causes IBM and Ponemon’s Case of Data Breach Study:
Human Errors (27%)
Human errors such as mere negligence can become the reason behind large data breaches. This can happen when employees or contactors are not focused on their jobs and make mistakes. Human errors account for 27% of the total breaches in the report. Establishing comprehensive systematic mechanisms can detect minor mistake before they result in data breaches. Overall, human errors cause the loss of $128 for each user in the organizaton.
System Glitches (25%)
As a product by humans, software can get make mistakes too. System glitches can cause major data breaches if proper mechanism isn’t established to control them. In the report, experts found system glitches to be responsible for a quarter of total data breaches. System glitches can incur damages up to $131 for every user.
Malicious Cyber Attacks (48%)
This is perhaps the most easily identifiable cause for a data breach. Hackers target businesses with malicious intent to breach data and incur losses to organizations. These people look for weaknesses in a system and use these weak sports to gain access to systems.
Sometimes cybercriminals can extend breaches caused by human error or system glitches. These attacks normally have SQL injections, phishing or social engineering, and insiders that turn rogue. Security experts at IBM estimate these attacks cost $157 for each user.
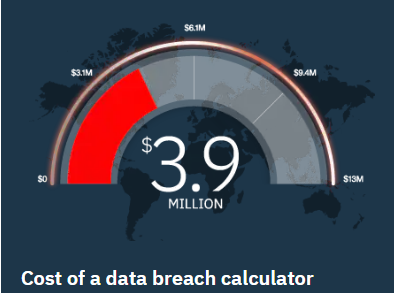
5. The average cost of data breaches worldwide is 3.6 million.
The Cost of a Data Breach Study further suggests data breaches cost 3.6 million on average worldwide. This is an alarming figure; however, latest reports suggest that these numbers are growing.
For the latest version of the study, IBM and Ponemon Institute further investigated these matters. They interviewed over 2200 data protection and compliance professionals that were members of 477 different companies. These professionals had suffered a data breach at least once in the past 12 months.
The study found that the cost of data breach was at $3.9 million on average. This means that the global cost had increased at almost 6.4% in just 12 months.
6. Experts predict that the global cost of cybercrime will grow past $2 trillion this year.
The “Future of Cybercrime Security: Financial and Corporate Threats & Mitigation” report by Juniper Research unearths some alarming predictions.
According to the report, global cybercrime cost will exceed the total $2 trillion in 2019. This estimation is four times the figure of what the same report predicted just four years ago in 2015.
7. Ransomware attacks are increasing at the rate of 350% every year.
As we all know, a ransomware is malicious software that hijacks a computer and holds it hostage. The system stay inoperable until the affected organization listens to hacker’s demands.
Cisco reports that these attacks have increasing at an express rate. People have to be sure that they protect their devices with necessary security mechanisms.
8. Grayware carries a more dangerous threat to mobile users than mobile malware.
One of the world’s biggest security giants – Symantec, issued the Internet Security Threat Report in 2018. The report suggests that mobile malware is increasing. The number of new variants of mobile malware has increased by 54% in just a single year.
This is worrisome because only 20% of Android devices run on the latest release. The overwhelming majority of mobile devices are still running on old versions. Older systems are not equipped with security mechanisms to deal with new threats.
Despite the alarming situation of mobile malware, grayware poses a greater threat. Grayware are applications that look safe on the outside but put user privacy at risk. These applications are often the ones that ask excessive permissions to support new features. The Symantec study found that almost 63% of grayware applications leak the user’s phone number.
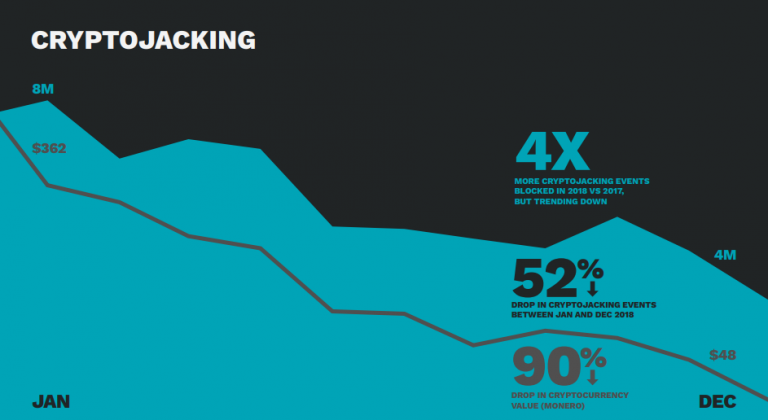
9. Cryptojacking is the one of the most dangerous cyber threats in 2020.
It’s alright if you haven’t heard of the phrase “cryptojacking” before. The term was recently coined (no pun intended) after the rise of cryptocurrencies.
The emergence of cryptocurrencies kick started a race between crypto-miners to earn coins. Miners need extensive amount of computing to mine these crypto-coins. As a result, some miners turned to malpractice to get more coins for themselves. They started hijacking CPUs to perform mining for them.
Symantec’s recent Internet Security Threat Report highlighted the increase in cryptojacking. The report suggests that cryptojacking events increased four times over in 2018 than 2017. Cryptojacking was at its height during first two months of 2018. Norton by Symantec claims to block 16 million attempts of cryptojacking during this period.
10. Almost 1.77 billion records got leaked only in January 2020.
This year has barely reached its quarter yet the data 2020 faced its fair share of data leaks in its first month alone. IT Governance reported that as much as 1,769,185,063 user record got leaked in the month of January.

The data in used in this record of breaches include the infamous Collection #1 data breach. This breach contained sensitive data such as username and password of almost 772 million people. Experts consider this breach to be monumental and consider it to be one of the biggest data breaches to happen.
Another data breach resulted from a MongoDB instance worth 854 GB of data. This database breach exposed CVs that contained confidential information about 202 million Chinese workers. This list of data breaches also included an Oklahoma government data breach. This breach resulted in the leak of 7 years worth of FBI investigations.
11. Groups using destructive malware have increased by 25% in 2018.
Seeing malware attacks increase is worrisome. However, destructive malware are far more dangerous than their conventional counterparts. Destructive malware targets are designed to target and destroy computer systems. These malware specialize in disabling computer systems from inside and making them inoperable.
Symantec’s 2019 report further suggests an increase in the number of groups that use destructive malware. The report highlights that these groups have increased by 25% in 2018. There have been several instances of destructive malware use in 2018.
Notable attacks include the Iran-based Chafer group disabling a Middle East service provider. The Thrip group crippled a satellite communication operator making it useless.
12. Experts predict that ransomware will cost organizations and businesses $11.5 billion this year.
The WannaCry ransomware attack in 2017 was depressing for its victims. Their list of casualties included critical organizations such as the British National Health Service. In addition, almost 200,000 computers in 150 countries suffered from this attack. People estimate that these attacks incurred damages that cost billions of dollars.
Over the years, other ransomware attacks have emerged to the scene. Ransomware attacks such as CryptoLocker, CryptoWall, TeslaCrypt were hot in the days cryptocurrency was at its height. Even now we cannot expect these ransomware attacks to decrease any time soon.
13. Malicious phishing emails account for 9 out of 10 cyber attacks.
As part of their research, PhishMe traced the origins of successful cyber attacks. The research included 40 million malicious emails sent to over 1000 organizations. In the end, the research found that 91% of successful cyber attacks were spearheaded by a phishing email. What’s more worrying than this statistic is that these attacks are on the rise.
14. 92% of total malware gets delivered through emails.
Verizon’s Breach Investigation Report for 2018 adds weight to PhishMe’s findings. The study found emails to be responsible for delivering 92% of total malware. Verizon group had analyzed 53,308 cyber security incidents and over 2,200 data breaches in 60+ countries.
The group found that emails were responsible for 92.4% of malware. Despite the immense number of malicious websites in the web, the web only had a minute contribution. The total contribution to malware from web was only 6.4%.
15. 76% of cyber attacks are financially motivated.
These days every aspect of life is getting interlinked with sophisticated devices and networks. From bank accounts to digital wallets, the trend of physical currency is shifting in today’s world. As online transactions become more common, cyber attacks are bound to increase.
So, it’s clear why the overwhelming majority of cyber attacks are motivated by money. Verizon’s Breach Investigation Report mentioned above also found that 76% of these attacks are financially motivated.
16. Hackers increased IoT attacks by 600% in 2017.
These days, almost every person has a smart phone. This means that hackers now have greater number of targets. With the emergence of the Internet of Things, there will be more devices that have limited security mechanisms.

Symantec highlighted that IoT attacks saw an increase of 600% between 2016 and 2017. Hackers can target IoT devices as soft entry points to invade a system and make intrusive changes. According to the Symantec’s 2019 Internet Security Report, an IoT device is a hacker’s best friend.
17. 31% organizations experience cyber attacks on operational structure.
Cisco reports that 31% of organizations experience an attack on operational structures. This low figure indicates that most organizations don’t experience cyber attacks.
However, speculation leads to believe that this figure is lower than it is in reality. Cyber attacks going unreported is a concerning factor for the security industry.
18. Over 500 employees in 65% companies never change passwords.
Most people don’t realize how risky it is to not change passwords once in a while. Hackers can break through passwords if they are not changed every once in a while. Varonis reports that 65% of the companies they reported have 500 employees that have never changed passwords.
Few people are at risk of getting their Instagram account attacked. However, businesses are far more critical and have immense capital invested in them. Even if a hacker manages to get a single employee’s sensitive information, they can use it as an entry point to break into the system.
19. Over 24,000 malicious mobile applications get blocked in various play stores every day.
Symantec reported that over 24,000 malicious mobile applications get blocked in various play stores every day. Hackers realize that almost everyone nowadays uses smart phones. For this reason, they target users by releasing malicious mobile applications in play stores.

Apple does a good job at regulating its play store applications. Its play store does not allow
harmful applications to download on iOS devices.
However, Android play store have a harder time spotting these problems. The reason behind this is the sheer amount of devices available on Android. Still, Android is doing a lot get around this problem.
Some malicious applications can get downloaded on both these platforms. However, they warn all users to not download any applications from unverified third party sources.
20. A business can get attacked by a ransomware every 13.275 seconds.
Cyber Defense Magazine reports that a business can business can get attacked by a ransomware every 13.275 seconds. Though this speed is not humanly possible, hackers can use automation to increase the frequency of their attacks. Attacks that fail to achieve their targets are relentlessly barraged again with improved capabilities to affect systems.
However, security systems fight fire with dire to take care of these issues. Many security applications now use automation to stop these kinds of attacks.
21. Cisco’s Talos unit warned that half a million router had been compromised by a cyber attack in May 2018.
Cisco’s cybersecurity wing – Talos announced that almost 500,000 routers across 54 countries had been infected with malware in May 2018. The organization believed that the attack was allegedly state-sponsored. First spotted in Ukraine, the attack used a sophisticated malware system known as VPNFilter.
Protect Your Internet Browsing
GET NORD VPN NOW!

98%
OVERALL RATING

Advertising Disclosure
The information we provide you is free of charge and a result of extensive research by our product experts. We use affiliate links in our site that provide us with referral commissions. While this fact may not influence the information we provide, it may affect the positioning of this information.